Kiln Process
Thermochemical Reactions in Cement Manufacturing
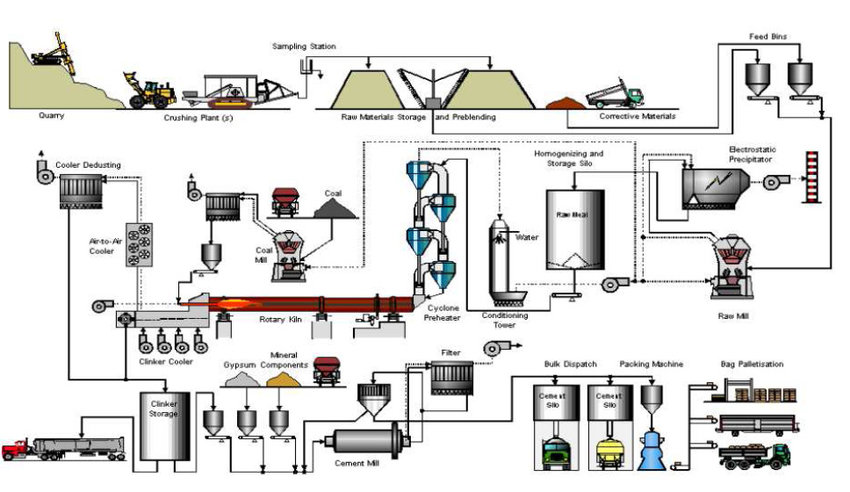
Kiln Process Thermochemical Reactions
Temperature ranges and chemical reactions in the kiln process
| Process | Reactions | Temperature °C | Temperature °F |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying/Pre-heat | Free water evaporates | 20 - 100 | 68 - 212 |
| Crystallization water driven out | 100 - 300 | 212 - 572 | |
| Chemical water driven out | 400 - 900 | 752 - 1652 | |
| Calcining | CO₂ Driven out CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ |
600 - 900 | 1112 - 1652 |
| Sintering/Clinkering | Formation of Liquid Phase, Formation of alite and belite | 1450 (exothermic) | 2642 (2440 - 2642) |
| Cooling | Crystallization of aluminates and ferrites | 1300 - 1240 | 2264 - 2372 |
Important Note:
Carbon Steel Temperature limit: 800°F (427°C). Refractory lining is required above this temperature.
Generalized Diagram of Long Dry Process Kiln
Dehydration Zone
Free water evaporates, formation of initial compounds
Gas Temp:
450°C / 840°F
450°C / 840°F
Material Temp:
50°C / 120°F
50°C / 120°F
Calcination Zone
Limestone decomposition, CO₂ release
Gas Temp:
800°C / 1470°F
800°C / 1470°F
Material Temp:
600°C / 1110°F
600°C / 1110°F
Clinkering Zone
Formation of C₂S and C₃S, liquid phase formation
Gas Temp:
1200°C / 2190°F
1200°C / 2190°F
Material Temp:
1000°C / 1830°F
1000°C / 1830°F
Cooling Zone
Rapid cooling of clinker, crystallization
Gas Temp:
1750°C / 3180°F
1750°C / 3180°F
Material Temp:
1350°C / 2460°F
1350°C / 2460°F
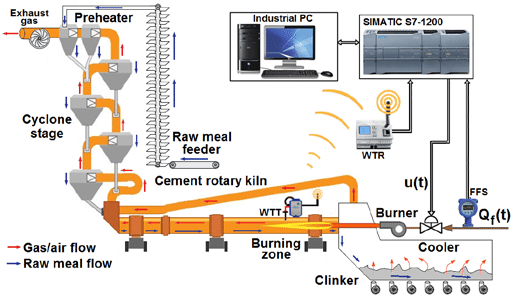
Preheater System
Preheater Tower
Preheaters perform 40-80% calcination
- Multiple stages for heat exchange
- Counter-current gas flow
- Efficient heat recovery system
- Reduces fuel consumption
Precalciner
Precalciners perform 70-96% calcination
- Higher calcination efficiency
- Separate combustion chamber
- Reduces kiln thermal load
- Increases production capacity
Factors Affecting Calcination
The difference between preheater and precalciner performance depends on:
- Number of preheater stages
- Type of calciner design
- Available kiln length
- Fuel type and quality
Rotary Kiln Specifications
Rotary Kiln
Key Components
Physical Structure
- Thick steel cylinder lined with refractory materials
- Diameter: 3m to 8m
- Length: 30m to 200m
- Mounted on roller bearings
- Rotates about its own axis at specified speed
Fuel Types
- Powdered coal
- Fuel oil
- Natural gas
- Alternative fuels (waste-derived)
Operating Temperature:
Up to 1500°C in the hottest zone
Physical and Chemical Changes in the Rotary Kiln
150°C
Limestone loses water in its combination
450°C
Clay decomposes
2SiO₂·Al₂O₃·2H₂O → 2SiO₂ + Al₂O₃ + 2H₂O ↑
650°C
Magnesium carbonate decomposes
MgCO₃ → MgO + CO₂ ↑
950°C
Calcium carbonate decomposes
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ ↑
1250°C
20-30% of raw materials become slurry, clinker balls start to form
Final Step
Grinding clinker with 2-3% gypsum to produce cement
Clinker Cooling Process
Cooling Requirements
Moderate rate of cooling results in higher strength clinker.
Stage 1: Rapid Cooling
From 1200°C to 500°C in approximately 15 minutes
Stage 2: Slow Cooling
From 500°C to normal atmospheric temperature in approximately 10 minutes
Rate of Cooling Influences:
- The degree of crystallization
- The size of the crystal
- The amount of amorphous materials present in clinker
Clinker Cooler
Controlled cooling for optimal clinker quality
Learn More About Cement Production
Explore the complete cement manufacturing process
Cement Process Our Products